

The next generation Wi-Fi standard is almost ready for final certification, which means that our wireless connection speeds could possibly increase significantly in 2024. This will make it easier for manufacturers of wireless hardware to start implementing the standard and putting it into laptops, smartphones, and smart home appliances. Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) is the replacement for Wi-Fi 6 and 6e. It should be certified in the upcoming months, but it will take some time for manufacturers to create products that work with it.
According to Tom’s Hardware, the Wi-Fi Alliance has declared that the Wi-Fi 7 standard’s specifics will be finalized by the end of Q1 2024. In order to enable businesses to produce wireless routers, client adapters, smartphone chips, and other goods that are compatible, this will enable the standard for compatible devices to be finalized and codified. Although some Wi-Fi 7 products have already been released, they were developed using the draft rather than the final specifications. They should still function with upcoming gadgets that support the new standard, though. Even so, they might not be able to use the entire performance permitted by the final standard, depending on their requirements.
The main benefit of Wi-Fi 7 is that it will enable a significant performance boost over Wi-Fi 6. With Wi-Fi 7, the potential maximum throughput can reach around 40Gb/s, compared to 9.6Gb/s with the current Wi-Fi 6e standard. However, that is the access point’s speed, therefore overhead will cause the real client device performance to be lower. It will utilize the 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz frequency bands, just like Wi-Fi 6e. Wi-Fi 6e was allowed to use the 6GHz band by the FCC in 2020, but devices are just now beginning to support it, so things take time.
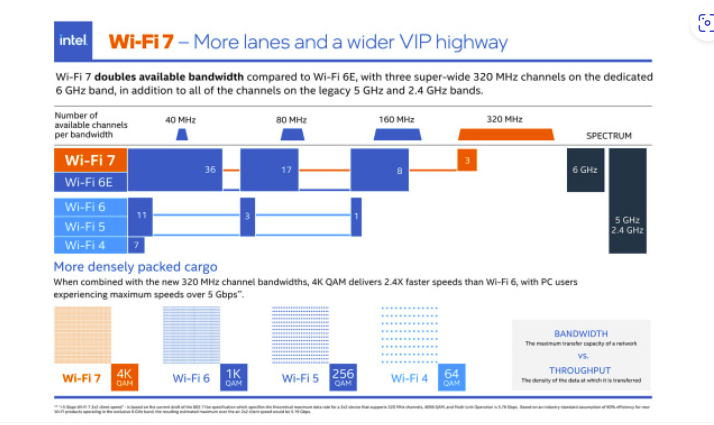
While Wi-Fi 6e topped out at 160MHz channels, the most notable new feature is the advent of three channels on the ultra-wide 320MHz band. In certain cases, this should provide twice the bandwidth of its predecessor. To guarantee maximum transmission speeds, suitable devices can also flip between all three spectrums. Additionally, 4K QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) is a feature of Wi-Fi 7, an improvement above 1K in Wi-Fi 6, according to Intel, enabling 2.4X greater transmission rates.
Even if the specification is almost complete, it will take a year or two, if not three, before any devices that support it become widely available. Although it was first introduced in 2019, Wi-Fi 6 is still present in new gadgets today. As Wi-Fi 7 devices become more commonplace over the course of the next year, the majority of high-end devices will no longer support Wi-Fi 6e. Although Wi-Fi 7 routers are now available on the market, as far as we know, there are no client adapters. Although a Wi-Fi 7 router isn’t capable of those speeds, it is at least future-proof. No one without a suitable access point and client adapter can reach Wi-Fi 7 performance. We anticipate that by late 2024 or early 2025, it will start to happen.